
Non-woven Fabrics: Definition, Manufacturing Processes, Raw Materials, and Applications
2025-01-10 15:24
1. Definition and Classification of Non-woven Fabrics:
● Non-woven fabrics are materials formed by bonding together short fibers (staple fibers) and long fibers (continuous filaments) through chemical, mechanical, thermal, or solvent treatments.
● They differ from traditional woven and knitted fabrics in having unique production processes and application ranges.
● Based on the manufacturing process, non-woven fabrics can be categorized into various types such as spunlace, needle-punched, spunbond, thermally bonded, wet-laid, and melt-blown non-woven fabrics.
2. Manufacturing Processes:
● Spunlace Non-woven Fabric: High-pressure water jets entangle fibers to form a fabric with certain strength and toughness. Widely used in facial mask materials and medical non-wovens.
● Needle-punched Non-woven Fabric: Repeatedly piercing the fiber web with hooked needles to interlock the fibers, creating a robust structure. Commonly used in geotextiles and carpet backings.
● Spunbond Non-woven Fabric: Melt-extruding, stretching into filaments, laying them into a web, and then bonding them thermally or chemically to form a fabric. Suitable for shopping bags and packaging materials.
● Thermally Bonded Non-woven Fabric: Heating the fiber web with hot air or rollers to partially melt the fiber surfaces and bond them together. Commonly used in baby diapers and sanitary napkins.
● Wet-laid Non-woven Fabric: Evenly distributing a fiber suspension on a screen, then pressing and drying it to form a fabric. Suitable for filter materials and battery separators.
● Melt-blown Non-woven Fabric: Using high-speed hot air to blow molten polymer into fine filaments, which are randomly distributed and cooled to form a fabric. Widely used in air and liquid filtration.

3. Raw Materials:
● The primary raw materials for non-woven fabrics include natural fibers like cotton and jute, regenerated fibers like bamboo fiber, synthetic polymers such as PP (polypropylene), PE (polyethylene), PET (polyethylene terephthalate), and high-performance new material fibers like carbon fiber, aramid fiber, quartz fiber, and basalt fiber.
● The choice of these materials depends on the end product's intended use and performance requirements. For example, medical-grade non-woven fabrics typically use high-purity synthetic fibers to ensure sterility and low allergenicity; carbon fiber and aramid fiber are ideal choices for applications requiring high strength and heat resistance.

4. Wide Range of Applications:
● Medical Field: Non-woven fabrics are used to make N95 masks, surgical gowns, drapes, medical sheets, and other protective equipment to ensure the safety of healthcare workers and patients.
● Hygiene Field: Used in producing diapers, wipes, sanitary napkins, incontinence products, and other personal care items, providing comfort and convenience.
● Industrial Field: Employed as filter materials (such as air filters, liquid filters), packaging materials (such as shopping bags, food packaging), and construction waterproof materials.
● Agricultural Field: Used as greenhouse covering materials, crop protection materials, etc., to help improve crop growth efficiency and yield.
● Home and Lifestyle Field: Used to make home textiles such as tablecloths, curtains, bedding, etc., enhancing quality of life.

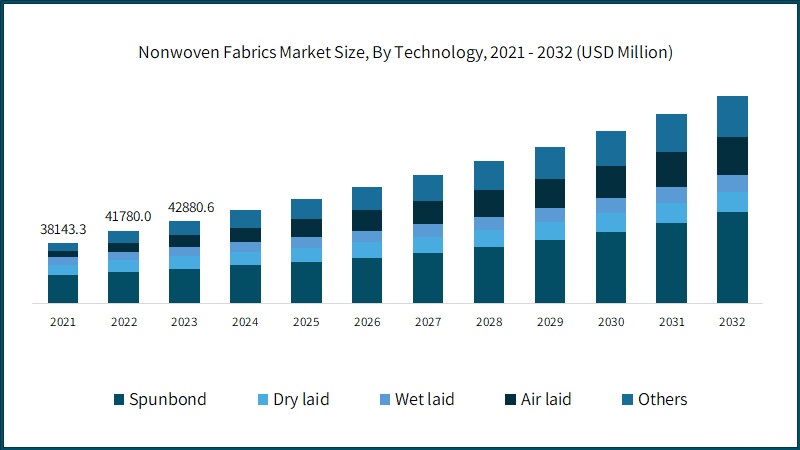
5. Market Forecast:
● According to market research reports, the growth trend indicates that the non-woven fabric industry has strong market potential and broad development space.
● With increasing awareness of health and environmental protection, the application of non-woven fabrics in medical, hygiene, and environmental protection fields will further expand.
In summary, non-woven fabrics, as an important textile material, not only have widespread applications in traditional fields but also show great potential in emerging areas. With continuous technological advancements and increasing market demand, the non-woven fabric industry will face more opportunities and challenges. In the future, non-woven fabrics will play an increasingly important role in medical, hygiene, industrial, agricultural, and other fields, promoting the development of related industries.









